Reporting MannWhitneyWilcoxontest results from SPSS YouTube
Reporting MannWhitneyWilcoxontest results from SPSS YouTube

The Mann Whitney U test, sometimes called the Mann Whitney Wilcoxon Test or the Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test, is used to test whether two samples are likely to derive from the same population (i.e., that the two populations have the same shape). Some investigators interpret this test as comparing the medians between the two populations. Recall that.
MannWhitney U Test in SPSS Statistics Setup, Procedure & Interpretation Laerd Statistics
The Mann-Whitney U test was applied to test if there were differences in engagement score between male and female groups. Since the shapes of distribution of engagement scores for two groups were not similar, we could conclude the engagement scores for females (mean rank = 17.75) and males (mean rank = 23.25) were not statistically.
So führen Sie einen MannWhitneyUTest in Stata durch • Statologie

1. Wilcoxon rank-sum test (or Mann-Whitney U test) The Wilcoxon rank-sum test (or the Mann-Whitney U test) is applied to the comparison of two independent data whose measurements are at least ordinal. The null hypothesis is that two sets of scores are samples from the same population; therefore they do not differ systematically. Steps of the.
MannWhitney U Test
This video shows how to conduct the Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon-test and interpret the results using R statistics. ️ Watch next: https://youtu.be/LcEj-r0uWLgGenera.
MannWhitney U in SPSS YouTube

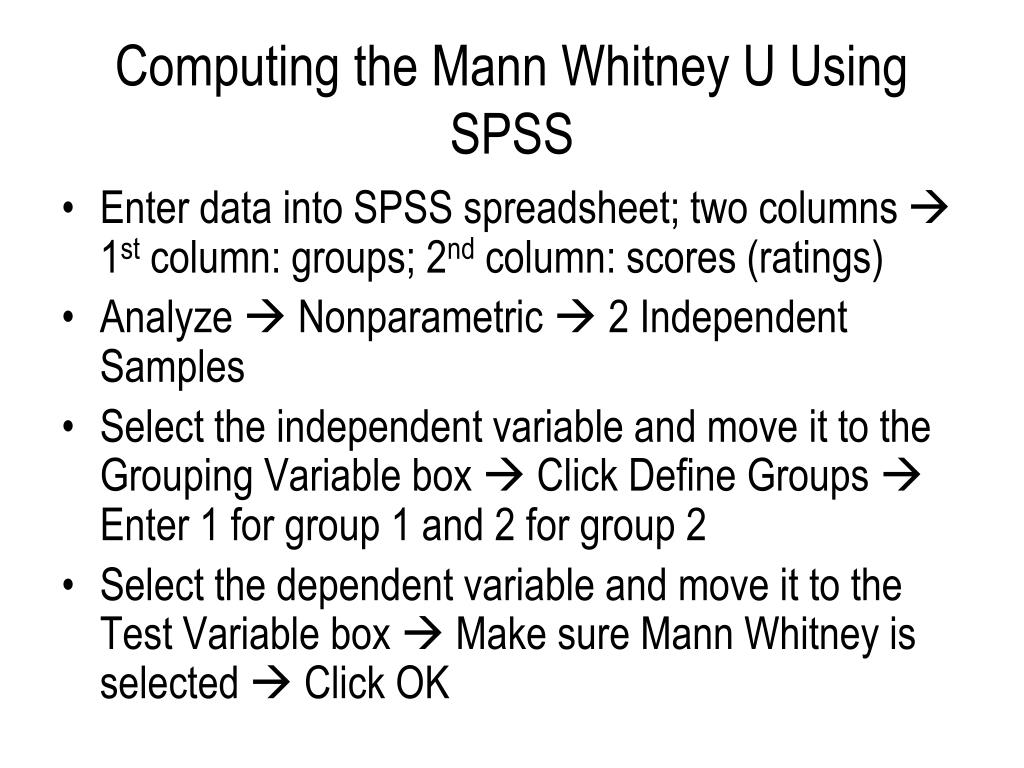
A Mann-Whitney U test (sometimes called the Wilcoxon rank-sum test) is used to compare the differences between two samples when the sample distributions are not normally distributed and the sample sizes are small (n <30). It is considered to be the nonparametric equivalent to the two sample t-test.. This tutorial explains how to perform a Mann-Whitney U test in SPSS.
The Mann Whitney U test (Wilcoxon Mann Whitney test) part 2/2 exact pvalue YouTube

The Mann-Whitney U test is used to compare differences between two independent groups when the dependent variable is either ordinal or continuous, but not normally distributed. For example, you could use the Mann-Whitney U test to understand whether attitudes towards pay discrimination, where attitudes are measured on an ordinal scale, differ.
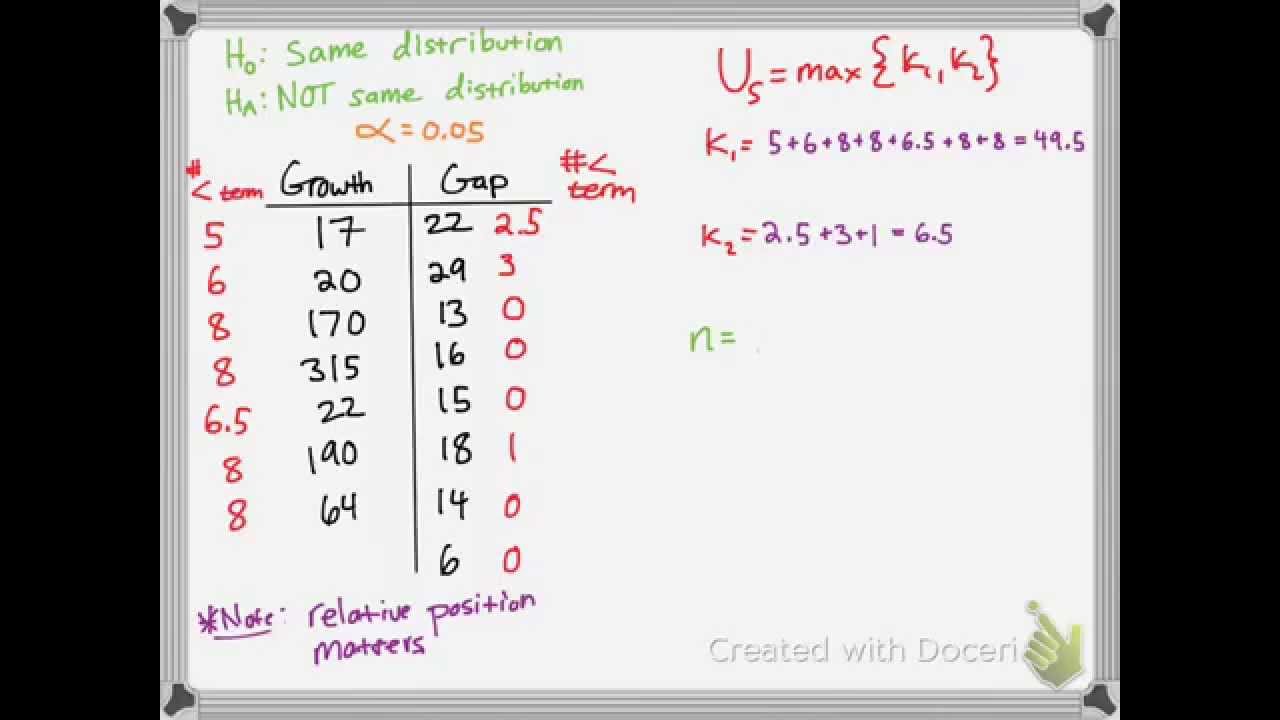
Mann Whitney U test Numerical Example with Step by Step Calculation Non Parametric

Two different types of test statistics can be used; both will result in the same test outcome. The first is the Wilcoxon rank sum statistic W W : W W = sum of ranks in group 1. The second type of test statistic is the Mann-Whitney U U statistic: U = W − n1(n1 +1) 2 U = W − n 1 ( n 1 + 1) 2. where n1 n 1 is the sample size of group 1.
WilcoxonMannWhitney Test YouTube
The Mann Whitney test will now decide on whether this difference in mean ranks is significant or not as is illustrated in the second table. The second SPSS output table contains details of the test itself and can be seen below: Te s t S t a t i s t i c s Science activities index Mann-Whitney U 2432391.000 Wilcoxon W 5101596.000 Z -9.439 Asymp. Sig.
How to Perform a MannWhitney U Test in SPSS Statology

Introduction. The Mann-Whitney U Test, or the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, is a powerful non-parametric test for comparing two independent samples. Unlike the traditional t-test, it does not require the assumption of normally distributed data. This test determines if the observations from one sample are typically bigger than those from the other.
test de mann whitney

The Mann Whitney U test is a nonparametric hypothesis test that compares two independent groups. Statisticians also refer to it as the Wilcoxon rank sum test. The Kruskal Wallis test extends this analysis so that can compare more than two groups. If you're involved in data analysis or scientific research, you're likely familiar with the t-test.
MannWhitney UTest / Wilcoxon Rangsummentest YouTube

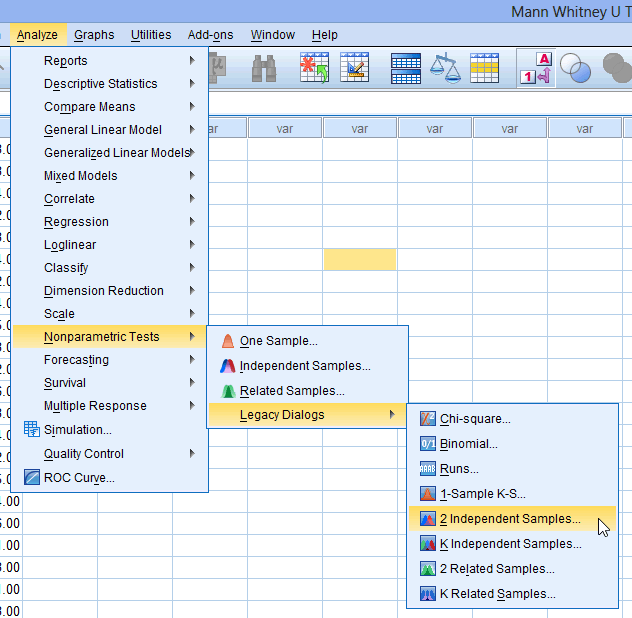
Step 1: Select the Mann-Whitney U Test option. Click the Analyze tab, then Nonparametric Tests, then Legacy Dialogs, then 2 Independent Samples: Step 2: Fill in the necessary values to perform the test. Drag mpg into the box labelled Test Variable List and group into the box labelled Grouping Variable. Click on Define Groups and define Group 1.
How to Perform a MannWhitney U Test in SAS Statology

Mann-Whitney test (also called the Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon (MWW/MWU), Wilcoxon rank-sum test, or Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test) is a nonparametric test of the null hypothesis that, for randomly selected values X and Y from two populations, the probability of X being greater than Y is equal to the probability of Y being greater than X.. Nonparametric tests used on two dependent samples are.
Mann Whitney Test Nonparametric Test in Minitab and SigmaXL Mann Whitney test in Minitab

SPSS produces a test statistics table to summarise the result of the Mann-Whitney U test. The key values are Mann-Whitney U, Z and the 2-tailed significance score. In our example, the No Dog group comprises greater than 20 observations. This means we can use the value of Z to derive our p-value. Otherwise, the significance value comes from U.
SPSS Note On Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test PDF MannWhitney U Test Median

For heavy‐tailed or very skewed distributions, use of the t ‐test is not recommended, especially for small sample sizes. For ordered categorical data, comparing averages by means of t ‐tests is not appropriate at all. For those situations, a nonparametric test such as the Wilcoxon‐Mann‐Whitney (WMW) test is much preferred.
PPT MannWhitney and Wilcoxon Tests PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3195361

The Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test evaluates the difference in medians between two similarly shaped populations, which have the same variance. This nonparametric test is similar to the two-sample Student's t Test. The primary differences are that the t Test requires the assumption of normality, while the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test can be performed where only rankings, that is, ordinal data, are.
PPT MannWhitney and Wilcoxon Tests PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6533537
SPSS Statistics Output and Interpretation. If you have been following this guide from page one, you will know that the following output and interpretation relates to the Mann-Whitney U test results when your two distributions have a different shape, such that you are comparing mean ranks rather than medians.This is what happens when your data has violated Assumption #4 of the Mann-Whitney U test.